Silicone Rubber
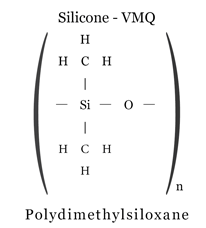 Silicone rubber is a semi-organic elastomer.
Silicone rubber is a semi-organic elastomer.
Resists temperature extremes, compression set, heat aging, ozone and water swell
Silicone resists extremes of temperature while resisting compression set and retaining flexibility. Silicone elastomers also provide very good resistance to heat aging, ozone and water swell.
Low physical strength and poor resistance to tearing and abrasion
Silicone demonstrates low physical strength, poor tear strength and poor abrasion resistance. These factors limit silicones’ use for static seal applications which require materials suitable for high friction.
Used in applications for extreme environments
Compared to conventional rubbers at extreme temperatures, silicone elastomers perform better with greater tensile strength, elongation, tear strength and compression set resistance but do not perform as well as some other elastomeric materials.
Also, compared to organic rubbers, silicone rubber displays good resistance to the sun’s UV light and the ozone this generates as well as good heat aging resistance. Unlike organic rubbers, silicone rubber has a low tensile strength and applications with even low imposed loads must be designed carefully.
Silicones are traditionally a more expensive option when compared to EPDM rubbers and thermoplastic elastomers.
Used for automotive applications, home goods, apparel, electronics and medical devices
Silicone rubber is generally non-reactive, stable and able to maintain its useful properties through a wide range of temperatures. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber is found in a wide variety of products, including: automotive applications, home goods (cooking, baking and food storage products), apparel (undergarments, sportswear and footwear), electronics, medical devices and implants and in home repair and hardware.



