Rubber Compression
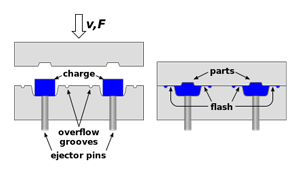
 The Rubber Compression Molding process begins with a sheet of solid, yet soft rubber that is placed in one half of a pre-heated mold cavity (usually by hand) of a two sided mold. The two halves of the mold are fitted together; pressure is applied so the compound within the mold is compressed to fill the mold cavity and form the part. Additional heat applied to the mold forces the rubber to further soften and disperse into all parts of the mold cavity and then heat the rubber to its vulcanization temperature. At a pre-determined time-at-temperature, the chemical reaction to change the rubber mixture to a homogenous compound (namely vulcanization), is complete and the finished rubber part is removed from the mold. The mold is cleaned and the process is repeated.
The Rubber Compression Molding process begins with a sheet of solid, yet soft rubber that is placed in one half of a pre-heated mold cavity (usually by hand) of a two sided mold. The two halves of the mold are fitted together; pressure is applied so the compound within the mold is compressed to fill the mold cavity and form the part. Additional heat applied to the mold forces the rubber to further soften and disperse into all parts of the mold cavity and then heat the rubber to its vulcanization temperature. At a pre-determined time-at-temperature, the chemical reaction to change the rubber mixture to a homogenous compound (namely vulcanization), is complete and the finished rubber part is removed from the mold. The mold is cleaned and the process is repeated.
 There are many advantages to using compression molding: low tooling cost, minimal waste (because the operator is able to accurately measure the amount of material to fit into the compression mold) and the ability to create intricate products (because high pressure from the compression forces the material to follow the mold to its exact design).
There are many advantages to using compression molding: low tooling cost, minimal waste (because the operator is able to accurately measure the amount of material to fit into the compression mold) and the ability to create intricate products (because high pressure from the compression forces the material to follow the mold to its exact design).
Compression molding is ideal for low production volumes of medium to large parts as well as for forming bulky parts of low to medium production volumes. Rubber compression molding is highly suited for gaskets, seals and o-rings.



